Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME)
The MSME sector contributes to 45% of India’s Total Industrial Employment, 50% of India’s Total Exports and 95% of all industrial units of the country and more than 6000 types of products are manufactured in these industries (As per msme.gov.in). When these industries grow, the economy of the country grows as a whole and flourishes. These industries are also known as small-scale industries or SSI’s.
Micro, Small and Medium sized enterprises in both the manufacturing and service sector can obtain MSME Registration under the MSMED Act. Though the MSME registration is not statutory, it is beneficial for business at it provides a range of benefits such as eligibility for lower rates of interest, excise exemption scheme, tax subsidies, power tariff subsidies, capital investment subsidies and other support.
What is the registration of MSME?
The Government of India has devised the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006. In legal terms, the definition of micro, small and medium enterprises can be best understood as
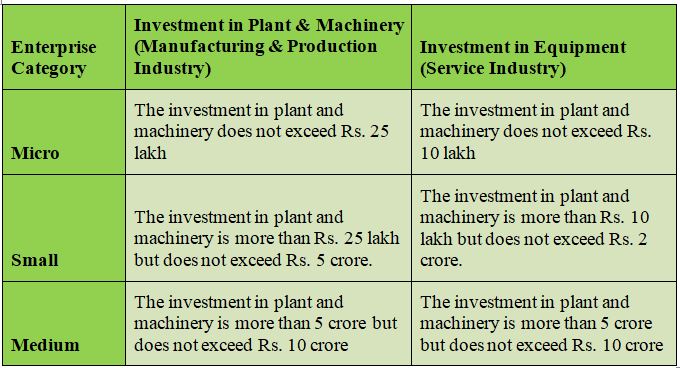
Any company that comes under the category of MSME needs t to ensure they are registered under the MSME category. MSME registration stands for the micro small and medium enterprises registration. MSMED Act has been launched by the government of India to support the MSME through various schemes, subsidies, and incentives. With MSME Registration, banks also provide loans at a lower rate of interest, as these MSME play an important role in the country’s economic growth.
Benefits of MSME Registration
- Due to the MSME registration, the bank loans become cheaper as the interest rate is very low around 1 to 1.5%. Much lower than interest on regular loans.
- There are various tax rebates offered to MSME.
- It also allowed credit for Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) to be carried forward for up to 15 years instead of 10 years
- There are many government tenders that are only open to the MSME Industries.
- They get easy access to credit.
- Once registered the cost of getting a patent done, or the cost of setting up the industry reduces as many rebates and concessions are available.
- Business registered under MSME is given higher preference for government license and certification.
- There is a One Time Settlement Fee for non-paid amounts of MSME.
Registration Process
- To do the registration the small and medium scale industry owner has to fill a single form which he can do online as well as offline.
- If a person wants to do registration for more than one industry then also he/she can do individual registration.
- To do the registration he/she has to fill a single form which is available at the website.
- The document required for the registration is Personal Aadhar number, Industry name, Address, bank account details and some common information.
- In this, the person can provide self-certified certificates.
- There is no registration fees required for this process.
- Once the detail-filled and upload you would be getting the registration number.
Documents required for MSME registration
Here are some essential documents we required to get the information about the organization and its activity:
- Aadha r Card of entrepreneur is must required
- Proprietorship PAN Card is required, if it is sole proprietorship firm
- Company PAN Card is required for Private Limited/ LLP/ OPC/ Partnership
- Certificate of Incorporation (COI) of company
- Address proof of business place
- Bank details (A/C Number, IFSC code)
- Nature of the business
- Investment of capital in business
- Number of employees working in your organization
Why we should do MSME Registration?
- Acquiring MSME registration certificate is not legally mandatory for a business or enterprise but you have to acquire the advantages, through it an organization can grow like a tree.
- So we will be advised you always that registering your enterprise under MSME scheme can get a variety of several benefits from the government sectors including lower interest rates, excise exemption scheme in respect to specified commodities, tax subsidies, exemption under Direct Tax Laws, power tariff subsidy, capital investment subsidies, etc.

